19.2: Kemia ya Uratibu wa Vyuma vya Mpito
- Page ID
- 182499
- Andika orodha ya sifa za kufafanua misombo ya uratibu
- Eleza miundo ya complexes iliyo na monodentate na ligands polydentate
- Tumia sheria za kawaida za majina ili kutaja misombo ya uratibu
- Eleza na kutoa mifano ya isomerism ya kijiometri na macho
- Kutambua matukio kadhaa ya asili na teknolojia ya misombo ya uratibu
Hemoglobin katika damu yako, chlorophyll katika mimea ya kijani, vitamini\(B_{12}\), na kichocheo kinachotumiwa katika utengenezaji wa polyethilini vyote vyenye misombo ya uratibu. Ions ya metali, hasa metali ya mpito, ni uwezekano wa kuunda tata. Wengi wa misombo hii ni rangi sana (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{1}\)). Katika salio la sura hii, tutazingatia muundo na ushirikiano wa misombo hii ya ajabu.

Kumbuka kwamba katika misombo kuu ya kipengele cha kikundi, elektroni za valence za atomi zilizotengwa huchanganya ili kuunda vifungo vya kemikali vinavyotimiza utawala wa octet. Kwa mfano, elektroni nne za valence za kaboni huingiliana na elektroni kutoka atomi nne za hidrojeni kuunda CH 4. Electron moja ya valence inacha sodiamu na inaongeza elektroni saba za valence za klorini ili kuunda kitengo cha formula ionic NaCl (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{2}\)). Transition metali si kawaida dhamana katika mtindo huu. Wao kimsingi huunda kuunganisha vifungo vya covalent, aina ya mwingiliano wa asidi-msingi wa Lewis ambapo elektroni zote mbili katika dhamana zinachangiwa na wafadhili (Lewis msingi) kwa kukubali elektroni (Lewis acid). Asidi ya Lewis katika complexes ya uratibu, mara nyingi huitwa ioni ya kati ya chuma (au atomi), mara nyingi ni chuma cha mpito au chuma cha mpito cha ndani, ingawa vipengele vikuu vya kikundi vinaweza pia kuunda misombo ya uratibu. Wafadhili wa msingi wa Lewis, wanaoitwa ligandi, wanaweza kuwa aina mbalimbali za kemikali-atomi, molekuli, au ioni. Mahitaji pekee ni kwamba wana jozi moja au zaidi ya elektroni, ambayo inaweza kuchangia kwa chuma cha kati. Mara nyingi, hii inahusisha atomi ya wafadhili na jozi moja ya elektroni ambayo inaweza kuunda dhamana ya kuratibu kwa chuma.
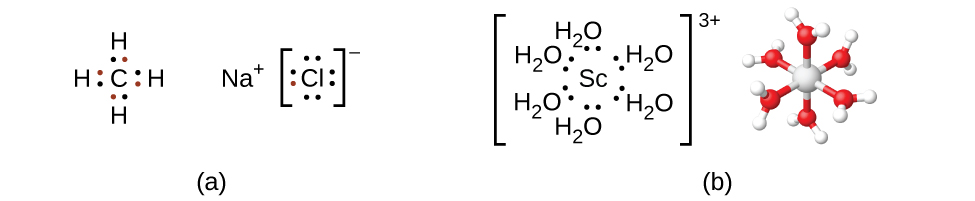
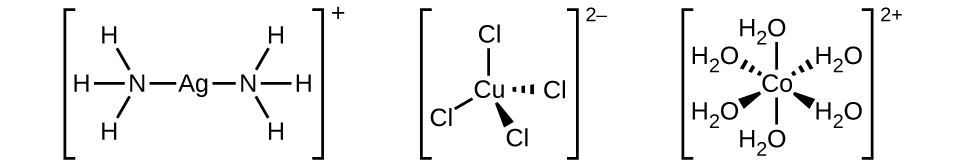
Tufe la uratibu lina ioni ya kati ya chuma au atomu pamoja na ligandi zake zilizounganishwa. Mabako katika formula hufunga nyanja ya uratibu; aina nje ya mabano si sehemu ya nyanja ya uratibu. Nambari ya uratibu wa ioni ya kati ya metali au atomi ni idadi ya atomi za wafadhili zilizounganishwa nayo. Nambari ya uratibu wa ion ya fedha katika [Ag (NH 3) 2] + ni mbili (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{3}\)). Kwa ioni ya shaba (II) katika [[CuCl 4] 2-, namba ya uratibu ni nne, ambapo kwa ioni ya cobalt (II) katika [Co (H 2 O) 6] 2+ namba ya uratibu ni sita. Kila moja ya ligandi hizi ni monodentati, kutoka Kigiriki kwa “toothed moja,” maana yake ni kwamba zinaungana na chuma cha kati kupitia atomi moja tu. Katika kesi hii, idadi ya ligands na namba ya uratibu ni sawa.
Ligands nyingine nyingi kuratibu na chuma katika mtindo ngumu zaidi. Ligandi za bidentate ni zile ambazo atomi mbili zinashirikiana na kituo cha chuma. Kwa mfano, ethylenediamine (en, H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2) ina atomi mbili za nitrojeni, ambayo kila mmoja ina jozi moja na inaweza kutumika kama msingi wa Lewis (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{4}\)). Atomi zote mbili zinaweza kuratibu na kituo kimoja cha chuma. Katika tata [Co (en) 3] 3+, kuna bidentate tatu sw ligands, na namba ya uratibu wa ioni ya cobalt (III) ni sita. Nambari za uratibu za kawaida ni mbili, nne, na sita, lakini mifano ya namba zote za uratibu kutoka 1 hadi 15 zinajulikana.
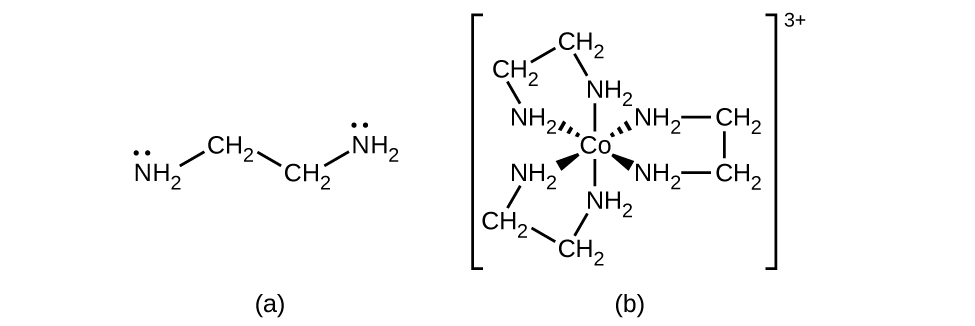
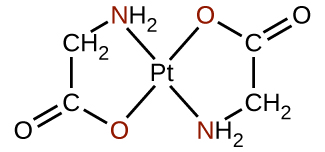
Ligand yoyote inayounganisha ioni ya kati ya chuma na atomi zaidi ya moja ya wafadhili ni ligand ya polidentati (au “meno mengi”) kwa sababu inaweza kuuma ndani ya kituo cha chuma na dhamana zaidi ya moja. Neno chelate (linalotamkwa “Key-marehemu”) kutoka Kigiriki kwa “claw” linatumika pia kuelezea aina hii ya mwingiliano. Ligandi nyingi za polidentati ni ligandi za chelating, na tata yenye moja au zaidi ya ligands hizi na chuma cha kati ni chelate. Ligand ya chelating pia inajulikana kama wakala wa chelating. Ligand ya chelating inashikilia ion ya chuma badala kama claw kaa ingekuwa kushikilia marumaru. Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{4}\) kilionyesha mfano mmoja wa chelate na tata ya heme katika hemoglobin ni mfano mwingine muhimu (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{5}\)). Ina ligand ya polidentati yenye atomi nne za wafadhili zinazoratibu kwa chuma.
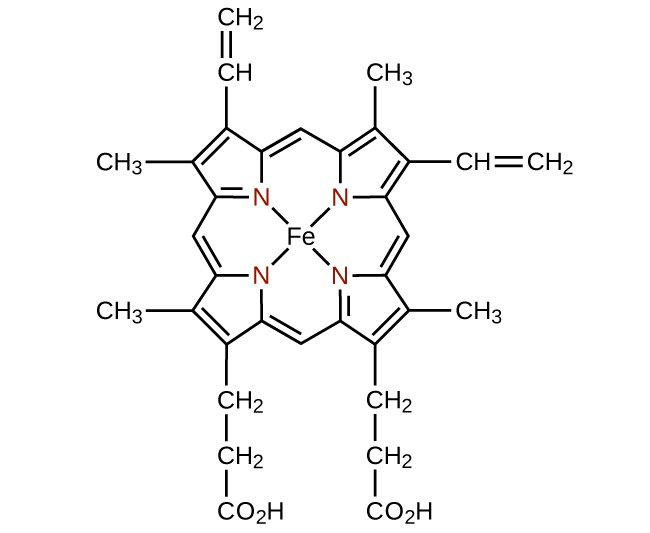
Ligandi za polidentati wakati mwingine hutambuliwa na viambishi awali vinavyoonyesha idadi ya atomi za wafadhili katika ligand. Kama tulivyoona, ligandi zilizo na atomi moja ya wafadhili, kama vile NH 3, Cl - na H 2 O, ni ligandi za monodentate. Ligands zilizo na makundi mawili ya wafadhili ni ligandi za bidentate. Ethylenediamine, H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2, na anion ya glycine asidi,\(\ce{NH2CH2CO2-}\) (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{6}\)) ni mifano ya ligands bidentate. Ligandi za tridentate, ligandi za tetradentate, ligandi za pentadentate, na ligandi za hexadentate zina atomi tatu, nne, tano, na sita za wafadhili, kwa mtiririko huo. Ligand ya heme (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{5}\)) ni ligand ya tetradentate.
Jina la Complexes
Nomenclature ya complexes ni mfano baada ya mfumo uliopendekezwa na Alfred Werner, mwanakemia wa Uswisi na mshindi wa Nobel, ambaye kazi yake bora zaidi ya miaka 100 iliyopita iliweka msingi wa uelewa wazi wa misombo hii. Sheria tano zifuatazo zinatumiwa kutaja complexes:
- Ikiwa kiwanja cha uratibu ni ionic, jina la cation kwanza na pili ya anion, kwa mujibu wa jina la kawaida.
- Jina la ligands kwanza, ikifuatiwa na chuma cha kati. Jina la ligandi kialfabeti. Ligandi hasi (anions) zina majina yaliyoundwa kwa kuongeza - o kwa jina la shina la kikundi (k.m\(\PageIndex{1}\). Kwa ligands nyingi za neutral, jina la molekuli hutumiwa. Tofauti nne za kawaida ni aqua (H 2 O), amine (NH 3), carbonyl (CO), na nitrosyl (NO). Kwa mfano, jina [Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 4] kama diaminetetrechloroplatinum (IV).
- Ikiwa zaidi ya ligand moja ya aina fulani iko, namba inaonyeshwa na viambishi awali di - (kwa mbili), tri - (kwa tatu), tetra - (kwa nne), penta - (kwa tano), na hexa - (kwa sita). Wakati mwingine, prefixes bis - (kwa mbili), tris - (kwa tatu), na tetrakis - (kwa nne) hutumiwa wakati jina la ligand tayari linajumuisha di -, tri -, au tetra -, au wakati jina la ligand linaanza na irabu. Kwa mfano, ion bis (bipyridyl) osmium (II) inatumia bis- kuashiria kwamba kuna ligands mbili zilizounganishwa na Os, na kila ligand ya bipyridyl ina makundi mawili ya pyridine (C 5 H 4 N).
| Ligand ya Anioniki | Jina |
|---|---|
| F - | fluoro |
| Cl - | kloro |
| Br - | bromo |
| Mimi - | iodo |
| CN - | siano |
| \(\ce{NO3-}\) | nitrato |
| OH - | haidrokso |
| O 2— | oxo |
| \(\ce{C2O4^2-}\) | oxalato |
| \(\ce{CO2^2-}\) | kabonato |
Wakati tata ni ama cation au molekuli ya upande wowote, jina la atomi ya kati ya chuma huandikwa hasa kama jina la elementi na hufuatwa na namba ya Kirumi katika mabano ili kuonyesha hali yake ya oksidi (Majedwali\(\PageIndex{2}\)\(\PageIndex{3}\),, na\(\PageIndex{3}\)). Wakati tata ni anion, suffix -ate imeongezwa kwenye shina la jina la chuma, ikifuatiwa na jina la Kirumi la hali yake ya oxidation.
| Mifano ambayo Complex Je, ni Cation | |
| [Co (NH 3) 6] Cl 3 | hexaaminecobalt (III) kloridi |
| [Pt (NH 3) 4 Cl 2] 2+ | tetraaminedichloroplatinum (IV) ion |
| [Ag (NH 3) 2] + | diaminesilver (I) ion |
| [Cr (H 2 O) 4 Cl 2] Cl | tetraaquadichlorochromium (III) kloridi |
| [Co (H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2) 3] 2 (SO 4) 3 | tris (ethylenediamine) cobalt (III) sulfate |
| Mifano ambayo Complex Je, ni Neutral | |
| [Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 4] | diaminetetrachloroplatinum (IV) |
| [Ni (H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2) Cl 2] | dichlorobis (ethylenediamine) nickel (II) |
| Mifano ambayo Complex Ni Anion | |
| [PtCl 6] 2 | hexachloroplatinate (IV) ion |
| Na 2 [S nCl 6] | hexachlorostannate ya sodiamu (IV) |
Wakati mwingine, jina la Kilatini la chuma hutumiwa wakati jina la Kiingereza ni clumsy. Kwa mfano, ferrate hutumiwa badala ya ironate, plumbate badala ya leadate, na stannate badala ya tinate. Hali ya oxidation ya chuma imedhamiriwa kulingana na mashtaka ya kila ligand na malipo ya jumla ya kiwanja cha uratibu. Kwa mfano, katika [Cr (H 2 O) 4 Cl 2] Br, nyanja ya uratibu (katika mabano) ina malipo ya 1+ ili kusawazisha ion ya bromidi. Ligandi za maji hazina upande wowote, na ligandi za kloridi ni anioni yenye malipo ya 1- kila mmoja. Kuamua hali ya oxidation ya chuma, tunaweka malipo ya jumla sawa na jumla ya ligands na chuma: +1 = -2 + x, hivyo hali ya oxidation (x) ni sawa na 3+.
Kuamua jina la complexes zifuatazo na kutoa idadi ya uratibu wa atomi ya kati ya chuma.
- Na 2 [PtCl 6]
- K 3 [C 2 O 4) 3]
- [Co (NH 3) 5 Cl] Cl 2
Suluhisho
- Kuna ioni mbili za Na +, hivyo nyanja ya uratibu ina malipo mawili hasi: [PtCl 6] 2-. Kuna sita ligands ya kloridi ya anionic, hivyo -1 = -6 + x, na hali ya oxidation ya platinamu ni 4+. Jina la tata ni hexachloroplatinate ya sodiamu (IV), na namba ya uratibu ni sita.
- Tufe la uratibu lina chaji ya 3- (kulingana na potasiamu) na ligandi za oksidi za oksidi kila mmoja huwa na chaji ya 2-, hivyo hali ya oksidi ya chuma inatolewa kwa -3 = -6 + x, na hii ni tata ya chuma (III). Jina ni trisoxalatoferrate ya potasiamu (III) (kumbuka kuwa tris hutumiwa badala ya tri kwa sababu jina la ligand linaanza na irabu). Kwa sababu oxalate ni ligand ya bidentate, tata hii ina idadi ya uratibu wa sita.
- Katika mfano huu, nyanja ya uratibu ina malipo ya cationic ya 2+. Ligand ya NH 3 haipatikani, lakini ligand ya chloro ina malipo ya 1-. Hali ya oxidation inapatikana kwa +2 = -1 + x na ni 3+, hivyo tata ni kloridi ya pentaaminechlorocobalt (III) na namba ya uratibu ni sita.
Dicyanoargenate tata ya potasiamu (I) hutumiwa kufanya misombo ya antiseptic. Kutoa formula na namba ya uratibu.
- Jibu
-
K [Ag (CN) 2]; uratibu namba mbili
Miundo ya Complexes
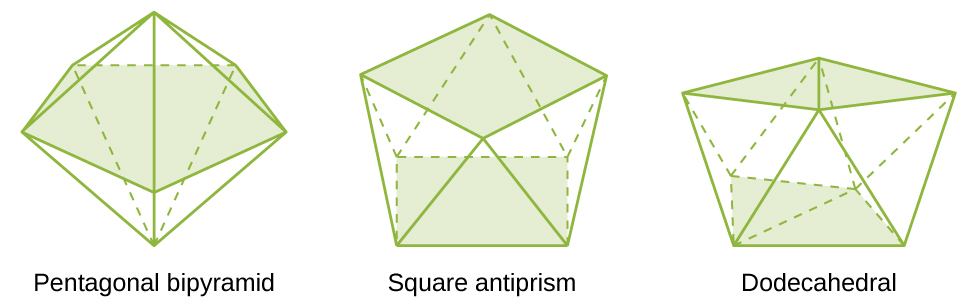
Miundo ya kawaida ya complexes katika misombo ya uratibu ni octahedral, tetrahedral, na mpango wa mraba (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{7}\)). Kwa complexes ya chuma ya mpito, nambari ya uratibu huamua jiometri karibu na ioni ya kati ya chuma. Jedwali\(\PageIndex{3}\) linalinganisha namba za uratibu kwa jiometri ya Masi:
| Idadi ya Uratibu | Jiometri ya Masi | Mfano |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | ya mistari | [Ag (NH 3) 2] + |
| 3 | mpango wa trigonal | [Cu (CN) 3] 2 |
| 4 | tetrahedral (d 0 au d 10), chini oxidation inasema kwa M | [Ni (CO 4)] |
| 4 | planar mraba (d 8) | [NiCl 4] 2- |
| 5 | bipyramidal ya trigonal | [Col 5] 2 |
| 5 | mraba piramidi | [VO (CN) 4] 2 |
| 6 | octahedral | [Col 6] 3 |
| 7 | bipiramidi ya pentagonal | [ZrF 7] 3 |
| 8 | mraba antiprism | [Ref 8] 2 |
| 8 | dodecahedron | [Mo (CN) 8] 4 |
| 9 na hapo juu | miundo ngumu zaidi | [Eh 9] 2 |
Tofauti na atomi za kikundi kikuu ambazo elektroni zote mbili za kuunganisha na zisizo za bonding zinaamua sura ya Masi, nonbonding d -elektroni hazibadili mpangilio wa ligands. Complexes ya Octahedral ina idadi ya uratibu wa sita, na atomi sita za wafadhili hupangwa kwenye pembe za octahedron karibu na ioni kuu ya chuma. Mifano ni inavyoonekana katika Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{8}\). Chloride na nitrati anions katika [Co (H 2 O) 6] Cl 2 na [Cr (en) 3] (NO 3) 3, na cations potassium katika K 2 [ptCl 6], ni nje ya mabano na si bonded kwa ion chuma.

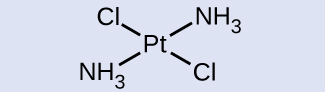
Kwa metali za mpito na namba ya uratibu wa nne, jiometri mbili tofauti zinawezekana: mpango wa tetrahedral au mraba. Tofauti na vipengele vikuu vya kikundi, ambapo jiometri hizi zinaweza kutabiri kutoka kwa nadharia ya VSEPR, majadiliano ya kina zaidi ya orbitals ya mpito ya chuma (kujadiliwa katika sehemu ya Theory ya Uwanja wa Crystal) inahitajika kutabiri ambayo complexes itakuwa tetrahedral na ambayo itakuwa mraba planar. Katika magumu ya tetrahedral kama vile [Zn (CN) 4] 2- (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{9}\)), kila jozi ya ligand huunda angle ya 109.5°. Katika complexes za planar za mraba, kama vile [Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 2], kila ligandi ina ligandi nyingine mbili kwenye pembe 90° (inayoitwa nafasi za cis) na ligand moja ya ziada kwenye angle ya 180°, katika nafasi ya trans.

Isomerism katika Complexes
Isomers ni aina tofauti za kemikali ambazo zina formula sawa ya kemikali. Mara nyingi metali za mpito huunda isoma za kijiometri, ambazo atomi zileile zinaunganishwa kupitia aina moja za vifungo lakini kwa tofauti katika mwelekeo wao angani. Complexes ya uratibu na ligands mbili tofauti katika nafasi za cis na trans kutoka ligand ya isomers fomu ya riba. Kwa mfano, octahedral [Co (NH 3) 4 Cl 2] + ion ina isoma mbili. Katika usanidi wa cis, ligands mbili za kloridi ziko karibu na kila mmoja (Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{1}\)). Isoma nyingine, Configuration trans, ina mbili ligands kloridi moja kwa moja katika kutoka kwa mtu mwingine.
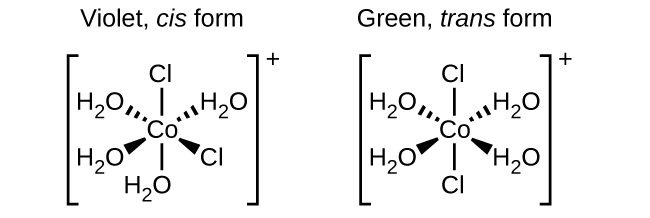
Isomers tofauti za kijiometri za dutu ni misombo tofauti ya kemikali. Wao huonyesha mali tofauti, ingawa wana formula sawa. Kwa mfano, isoma mbili za [Co (NH 3) 4 Cl 2] NO 3 hutofautiana na rangi; fomu ya cis ni violet, na fomu ya trans ni ya kijani. Zaidi ya hayo, isoma hizi zina wakati tofauti wa dipole, umumunyifu, na reactivities. Kama mfano wa jinsi mpangilio katika nafasi unaweza kuathiri mali Masi, fikiria polarity ya mbili [Co (NH 3) 4 Cl 2] NO 3 isomers. Kumbuka kwamba polarity ya molekuli au ion imedhamiriwa na dipoles ya dhamana (ambayo ni kutokana na tofauti katika electronegativity ya atomi bonding) na utaratibu wao katika nafasi. Katika isoma moja, ligands za kloridi za cis husababisha wiani zaidi wa elektroni upande mmoja wa molekuli kuliko nyingine, na kuifanya polar. Kwa isoma ya trans, kila ligand ni moja kwa moja hela kutoka ligand kufanana, hivyo dipoles dhamana kufuta nje, na molekuli ni nonpolar.
Tambua isoma ya kijiometri ya [Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 2] inavyoonekana kwenye Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{9}\) b Chora isoma nyingine ya kijiometri na upe jina lake kamili.
Suluhisho
Katika Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{9}\) b, ligands mbili za klorini zinachukua nafasi za cis. Fomu nyingine inavyoonyeshwa hapa chini. Wakati wa kutaja isomers maalum, descriptor imeorodheshwa mbele ya jina. Kwa hiyo, tata hii ni trans -diaminedichloroplatinum (II).
Isoma trans ya [Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 2] ina kila ligand moja kwa moja hela kutoka ligand karibu.
Chora ion trans -diaqua- trans -dibromo- trans -dichlorocobalt (II).
- Jibu
-
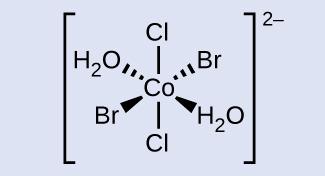
Cobalt iko katikati na wedges ya kushoto na ya kulia iliyounganishwa na bromini na H 2 O kwa mtiririko huo. Mistari ya dash ya kushoto na ya kulia imeunganishwa na H 2 O na bromini kwa mtiririko huo. Akizungumzia moja kwa moja hadi juu na chini kinyume na mtu mwingine ni klorini. Fomu nzima ya miundo imefungwa katika bracket mraba na superscript ya 2 hasi.
Aina nyingine muhimu ya isoma ni isoma za macho, au enantiomers, ambazo vitu viwili ni picha halisi za kioo za kila mmoja lakini haziwezi kuunganishwa ili sehemu zote zifanane. Hii ina maana kwamba isomers macho ni nonsuperimposable kioo picha. Mfano wa kawaida wa hii ni jozi ya mikono, ambayo mkono wa kulia na wa kushoto ni picha za kioo za kila mmoja lakini haziwezi kuingizwa. Isoma za macho ni muhimu sana katika kikaboni na biokemia kwa sababu mifumo hai mara nyingi huingiza isoma moja maalum ya macho na sio nyingine. Tofauti na isoma za kijiometri, jozi za isoma za macho zina mali zinazofanana (kiwango cha kuchemsha, polarity, umumunyifu, nk). Isoma za macho hutofautiana tu kwa njia zinazoathiri mwanga uliotiwa na jinsi wanavyoitikia na isoma nyingine za macho. Kwa complexes uratibu, wengi uratibu misombo kama vile [M (en) 3] n+ [ambayo M n+ ni kati chuma ion kama vile chuma (III) au cobalt (II)] fomu enantiomers, kama inavyoonekana katika Kielelezo\(\PageIndex{11}\). These two isomers will react differently with other optical isomers. For example, DNA helices are optical isomers, and the form that occurs in nature (right-handed DNA) will bind to only one isomer of [M(en)3]n+ and not the other.
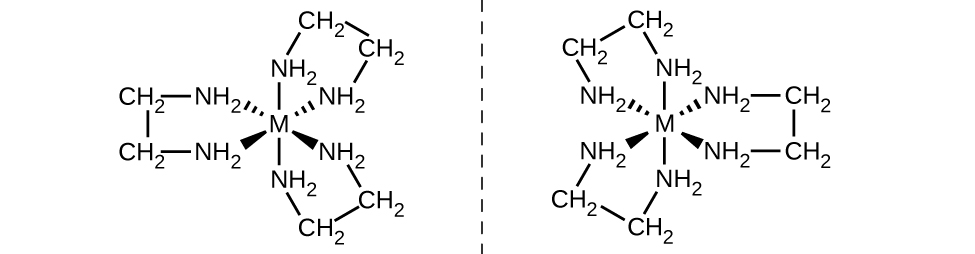
The [Co(en)2Cl2]+ ion exhibits geometric isomerism (cis/trans), and its cis isomer exists as a pair of optical isomers (Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)).

Linkage isomers occur when the coordination compound contains a ligand that can bind to the transition metal center through two different atoms. For example, the CN ligand can bind through the carbon atom (cyano) or through the nitrogen atom (isocyano). Similarly, SCN− can be bound through the sulfur or nitrogen atom, affording two distinct compounds ([Co(NH3)5SCN]2+ or [Co(NH3)5NCS]2+).
Ionization isomers (or coordination isomers) occur when one anionic ligand in the inner coordination sphere is replaced with the counter ion from the outer coordination sphere. A simple example of two ionization isomers are [CoCl6][Br] and [CoCl5Br][Cl].
Coordination Complexes in Nature and Technology
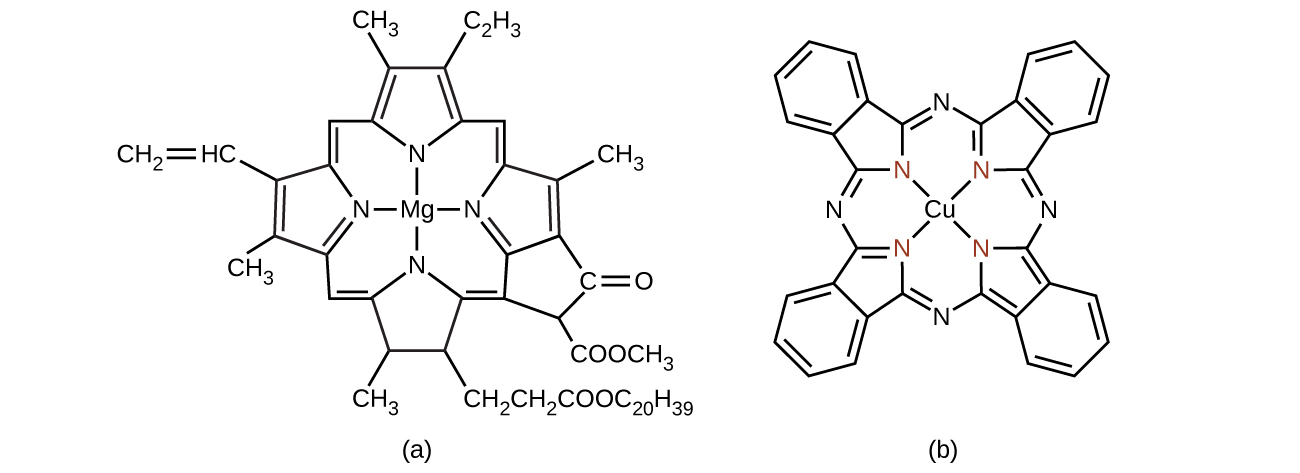
Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, is a complex that contains magnesium (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)). This is an example of a main group element in a coordination complex. Plants appear green because chlorophyll absorbs red and purple light; the reflected light consequently appears green. The energy resulting from the absorption of light is used in photosynthesis.
Transition Metal Catalysts
One of the most important applications of transition metals is as industrial catalysts. As you recall from the chapter on kinetics, a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy and is regenerated in the catalytic cycle. Over 90% of all manufactured products are made with the aid of one or more catalysts. The ability to bind ligands and change oxidation states makes transition metal catalysts well suited for catalytic applications. Vanadium oxide is used to produce 230,000,000 tons of sulfuric acid worldwide each year, which in turn is used to make everything from fertilizers to cans for food. Plastics are made with the aid of transition metal catalysts, along with detergents, fertilizers, paints, and more (Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)). Very complicated pharmaceuticals are manufactured with catalysts that are selective, reacting with one specific bond out of a large number of possibilities. Catalysts allow processes to be more economical and more environmentally friendly. Developing new catalysts and better understanding of existing systems are important areas of current research.

Many other coordination complexes are also brightly colored. The square planar copper(II) complex phthalocyanine blue (from Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)) is one of many complexes used as pigments or dyes. This complex is used in blue ink, blue jeans, and certain blue paints.
The structure of heme (Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)), the iron-containing complex in hemoglobin, is very similar to that in chlorophyll. In hemoglobin, the red heme complex is bonded to a large protein molecule (globin) by the attachment of the protein to the heme ligand. Oxygen molecules are transported by hemoglobin in the blood by being bound to the iron center. When the hemoglobin loses its oxygen, the color changes to a bluish red. Hemoglobin will only transport oxygen if the iron is Fe2+; oxidation of the iron to Fe3+ prevents oxygen transport.
Complexing agents often are used for water softening because they tie up such ions as Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe2+, which make water hard. Many metal ions are also undesirable in food products because these ions can catalyze reactions that change the color of food. Coordination complexes are useful as preservatives. For example, the ligand EDTA, (HO2CCH2)2NCH2CH2N(CH2CO2H)2, coordinates to metal ions through six donor atoms and prevents the metals from reacting (Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)). This ligand also is used to sequester metal ions in paper production, textiles, and detergents, and has pharmaceutical uses.
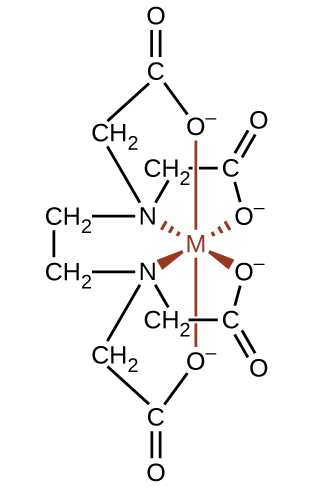
Complexing agents that tie up metal ions are also used as drugs. British Anti-Lewisite (BAL), HSCH2CH(SH)CH2OH, is a drug developed during World War I as an antidote for the arsenic-based war gas Lewisite. BAL is now used to treat poisoning by heavy metals, such as arsenic, mercury, thallium, and chromium. The drug is a ligand and functions by making a water-soluble chelate of the metal; the kidneys eliminate this metal chelate (Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)). Another polydentate ligand, enterobactin, which is isolated from certain bacteria, is used to form complexes of iron and thereby to control the severe iron buildup found in patients suffering from blood diseases such as Cooley’s anemia, who require frequent transfusions. As the transfused blood breaks down, the usual metabolic processes that remove iron are overloaded, and excess iron can build up to fatal levels. Enterobactin forms a water-soluble complex with excess iron, and the body can safely eliminate this complex.

Ligands like BAL and enterobactin are important in medical treatments for heavy metal poisoning. However, chelation therapies can disrupt the normal concentration of ions in the body, leading to serious side effects, so researchers are searching for new chelation drugs. One drug that has been developed is dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{18}\). Identify which atoms in this molecule could act as donor atoms.
Solution
All of the oxygen and sulfur atoms have lone pairs of electrons that can be used to coordinate to a metal center, so there are six possible donor atoms. Geometrically, only two of these atoms can be coordinated to a metal at once. The most common binding mode involves the coordination of one sulfur atom and one oxygen atom, forming a five-member ring with the metal.
Some alternative medicine practitioners recommend chelation treatments for ailments that are not clearly related to heavy metals, such as cancer and autism, although the practice is discouraged by many scientific organizations.1 Identify at least two biologically important metals that could be disrupted by chelation therapy.
- Answer
-
Ca, Fe, Zn, and Cu
Ligands are also used in the electroplating industry. When metal ions are reduced to produce thin metal coatings, metals can clump together to form clusters and nanoparticles. When metal coordination complexes are used, the ligands keep the metal atoms isolated from each other. It has been found that many metals plate out as a smoother, more uniform, better-looking, and more adherent surface when plated from a bath containing the metal as a complex ion. Thus, complexes such as [Ag(CN)2]− and [Au(CN)2]− are used extensively in the electroplating industry.
In 1965, scientists at Michigan State University discovered that there was a platinum complex that inhibited cell division in certain microorganisms. Later work showed that the complex was cis-diaminedichloroplatinum(II), [Pt(NH3)2(Cl)2], and that the trans isomer was not effective. The inhibition of cell division indicated that this square planar compound could be an anticancer agent. In 1978, the US Food and Drug Administration approved this compound, known as cisplatin, for use in the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Since that time, many similar platinum compounds have been developed for the treatment of cancer. In all cases, these are the cis isomers and never the trans isomers. The diamine (NH3)2 portion is retained with other groups, replacing the dichloro [(Cl)2] portion. The newer drugs include carboplatin, oxaliplatin, and satraplatin.
Summary
The transition elements and main group elements can form coordination compounds, or complexes, in which a central metal atom or ion is bonded to one or more ligands by coordinate covalent bonds. Ligands with more than one donor atom are called polydentate ligands and form chelates. The common geometries found in complexes are tetrahedral and square planar (both with a coordination number of four) and octahedral (with a coordination number of six). Cis and trans configurations are possible in some octahedral and square planar complexes. In addition to these geometrical isomers, optical isomers (molecules or ions that are mirror images but not superimposable) are possible in certain octahedral complexes. Coordination complexes have a wide variety of uses including oxygen transport in blood, water purification, and pharmaceutical use.
Footnotes
- National Council against Health Fraud, NCAHF Policy Statement on Chelation Therapy, (Peabody, MA, 2002).
Glossary
- bidentate ligand
- ligand that coordinates to one central metal through coordinate bonds from two different atoms
- central metal
- ion or atom to which one or more ligands is attached through coordinate covalent bonds
- chelate
- complex formed from a polydentate ligand attached to a central metal
- chelating ligand
- ligand that attaches to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms
- cis configuration
- configuration of a geometrical isomer in which two similar groups are on the same side of an imaginary reference line on the molecule
- coordination compound
- substance consisting of atoms, molecules, or ions attached to a central atom through Lewis acid-base interactions
- coordination number
- number of coordinate covalent bonds to the central metal atom in a complex or the number of closest contacts to an atom in a crystalline form
- coordination sphere
- central metal atom or ion plus the attached ligands of a complex
- donor atom
- atom in a ligand with a lone pair of electrons that forms a coordinate covalent bond to a central metal
- ionization isomer
- (or coordination isomer) isomer in which an anionic ligand is replaced by the counter ion in the inner coordination sphere
- ligand
- ion or neutral molecule attached to the central metal ion in a coordination compound
- linkage isomer
- coordination compound that possesses a ligand that can bind to the transition metal in two different ways (CN− vs. NC−)
- monodentate
- ligand that attaches to a central metal through just one coordinate covalent bond
- optical isomer
- (also, enantiomer) molecule that is a nonsuperimposable mirror image with identical chemical and physical properties, except when it reacts with other optical isomers
- polydentate ligand
- ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms, named with prefixes specifying how many donors are present (e.g., hexadentate = six coordinate bonds formed)
- trans configuration
- configuration of a geometrical isomer in which two similar groups are on opposite sides of an imaginary reference line on the molecule


