7.4: حل المشكلات
- Page ID
- 197967
أهداف التعلم
- وصف استراتيجيات حل المشكلات
- تعريف الخوارزمية والاستدلالية
- شرح بعض العوائق الشائعة لحل المشكلات بشكل فعال
يواجه الأشخاص مشاكل كل يوم - عادةً مشاكل متعددة على مدار اليوم. في بعض الأحيان تكون هذه المشاكل واضحة: لمضاعفة وصفة عجينة البيتزا، على سبيل المثال، كل ما هو مطلوب هو مضاعفة كل مكون في الوصفة. ومع ذلك، في بعض الأحيان، تكون المشاكل التي نواجهها أكثر تعقيدًا. على سبيل المثال، لنفترض أن لديك موعدًا نهائيًا للعمل، ويجب عليك إرسال نسخة مطبوعة من التقرير بالبريد إلى المشرف الخاص بك بحلول نهاية يوم العمل. التقرير حساس للوقت ويجب إرساله بين عشية وضحاها. لقد انتهيت من التقرير الليلة الماضية، لكن طابعتك لن تعمل اليوم. ماذا يجب أن تفعل؟ تحتاج أولاً إلى تحديد المشكلة ثم تطبيق استراتيجية لحل المشكلة.
استراتيجيات حل المشكلات
عندما تواجه مشكلة - سواء كانت مشكلة رياضية معقدة أو طابعة معطلة، كيف يمكنك حلها؟ قبل إيجاد حل للمشكلة، يجب أولاً تحديد المشكلة بوضوح. بعد ذلك، يمكن تطبيق واحدة من العديد من استراتيجيات حل المشكلات، ونأمل أن يؤدي ذلك إلى حل.
استراتيجية حل المشكلات هي خطة عمل تستخدم لإيجاد حل. الاستراتيجيات المختلفة لها خطط عمل مختلفة مرتبطة بها (انظر الجدول\(\PageIndex{1}\) أدناه). على سبيل المثال، الإستراتيجية المعروفة هي التجربة والخطأ. يصف القول المأثور القديم، «إذا لم تنجح في البداية، حاول، حاول مرة أخرى» التجربة والخطأ. فيما يتعلق بالطابعة المعطلة، يمكنك محاولة التحقق من مستويات الحبر، وإذا لم ينجح ذلك، يمكنك التحقق للتأكد من عدم انحشار درج الورق. أو ربما لم تكن الطابعة متصلة فعليًا بجهاز الكمبيوتر المحمول. عند استخدام التجربة والخطأ، ستستمر في تجربة حلول مختلفة حتى تحل مشكلتك. على الرغم من أن التجربة والخطأ ليست عادةً واحدة من أكثر الاستراتيجيات كفاءة من حيث الوقت، إلا أنها شائعة الاستخدام.
| الأسلوب | وصف | مثال |
|---|---|---|
| التجربة والخطأ | استمر في تجربة حلول مختلفة حتى يتم حل المشكلة | إعادة تشغيل الهاتف وإيقاف تشغيل WiFi وإيقاف تشغيل البلوتوث لتحديد سبب خلل هاتفك |
| خوارزمية | صيغة حل المشكلات خطوة بخطوة | دليل التعليمات لتثبيت برنامج جديد على جهاز الكمبيوتر الخاص بك |
| الاستدلالية | إطار عام لحل المشكلات | العمل بشكل عكسي؛ تقسيم المهمة إلى خطوات |
نوع آخر من الإستراتيجية هو الخوارزمية. الخوارزمية هي صيغة لحل المشكلات توفر لك تعليمات خطوة بخطوة تستخدم لتحقيق النتيجة المرجوة (Kahneman، 2011). يمكنك التفكير في الخوارزمية كوصفة تحتوي على تعليمات مفصلة للغاية تنتج نفس النتيجة في كل مرة يتم فيها تنفيذها. تُستخدم الخوارزميات بشكل متكرر في حياتنا اليومية، خاصة في علوم الكمبيوتر. عند إجراء بحث على الإنترنت، تستخدم محركات البحث مثل Google الخوارزميات لتحديد الإدخالات التي ستظهر أولاً في قائمة النتائج. يستخدم Facebook أيضًا خوارزميات لتحديد المنشورات التي سيتم عرضها على ملف الأخبار الخاص بك. هل يمكنك تحديد الحالات الأخرى التي تستخدم فيها الخوارزميات؟
الاستدلال هو نوع آخر من استراتيجيات حل المشكلات. في حين أنه يجب اتباع الخوارزمية بالضبط لإنتاج نتيجة صحيحة، فإن التوجيه هو إطار عام لحل المشكلات (Tversky & Kahneman، 1974). يمكنك التفكير في هذه الأمور على أنها اختصارات ذهنية تُستخدم لحل المشكلات. «القاعدة العامة» هي مثال على الاستدلال. توفر هذه القاعدة الوقت والطاقة للشخص عند اتخاذ القرار، ولكن على الرغم من خصائصها الموفرة للوقت، إلا أنها ليست دائمًا أفضل طريقة لاتخاذ قرار عقلاني. تُستخدم أنواع مختلفة من الاستدلال في أنواع مختلفة من المواقف، ولكن الدافع لاستخدام الاستدلال يحدث عند استيفاء أحد الشروط الخمسة (Pratkanis، 1989):
- عندما يواجه المرء الكثير من المعلومات
- عندما يكون وقت اتخاذ القرار محدودًا
- عندما يكون القرار الذي سيتم اتخاذه غير مهم
- عندما يكون هناك وصول إلى معلومات قليلة جدًا لاستخدامها في اتخاذ القرار
- عندما يتبادر إلى الذهن استطلاع مناسب في نفس اللحظة
يعد العمل بشكل عكسي طريقة إرشادية مفيدة تبدأ من خلالها في حل المشكلة من خلال التركيز على النتيجة النهائية. خذ بعين الاعتبار هذا المثال: أنت تعيش في واشنطن العاصمة وتمت دعوتك لحضور حفل زفاف\(\text{4 PM}\) يوم السبت في فيلادلفيا. مع العلم أن الطريق السريع\(95\) يميل إلى النسخ الاحتياطي في أي يوم من أيام الأسبوع، فأنت بحاجة إلى تخطيط مسارك ووقت مغادرتك وفقًا لذلك. إذا كنت ترغب في حضور حفل الزفاف\(\text{3:30 PM}\)، واستغرق الأمر\(2.5\) ساعات للوصول إلى فيلادلفيا بدون حركة مرور، فما هو الوقت الذي يجب أن تغادر فيه منزلك؟ أنت تستخدم أسلوب العمل الرجعي لتخطيط أحداث يومك بشكل منتظم، ربما دون حتى التفكير في الأمر.
طريقة إرشادية مفيدة أخرى هي ممارسة تحقيق هدف أو مهمة كبيرة عن طريق تقسيمها إلى سلسلة من الخطوات الصغيرة. غالبًا ما يستخدم الطلاب هذه الطريقة الشائعة لإكمال مشروع بحثي كبير أو مقال طويل للمدرسة. على سبيل المثال، عادةً ما يقوم الطلاب بتبادل الأفكار، وتطوير أطروحة أو موضوع رئيسي، والبحث في الموضوع المختار، وتنظيم معلوماتهم في مخطط تفصيلي، وكتابة مسودة أولية، ومراجعة المسودة الأولية وتحريرها، وتطوير مسودة نهائية، وتنظيم قائمة المراجع، وتصحيح أعمالهم قبل تسليم المشروع. تصبح المهمة الكبيرة أقل صعوبة عندما يتم تقسيمها إلى سلسلة من الخطوات الصغيرة.
EVERYDAY CONNECTION: Solving Puzzles
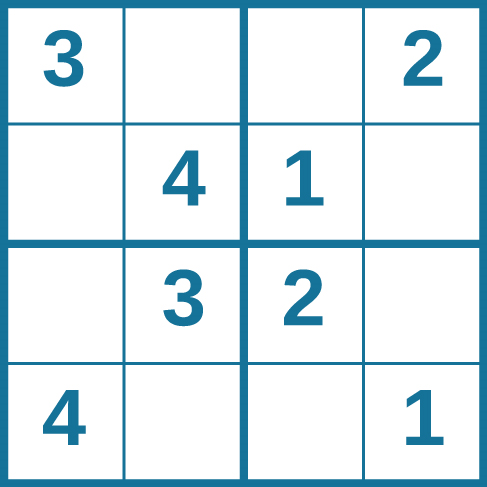
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a \(9\times 9\) grid. The simple sudoku below is a \(4\times 4\) grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: \(1\), \(2\), \(3\), or \(4\). Here are the rules: The numbers must total \(10\) in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
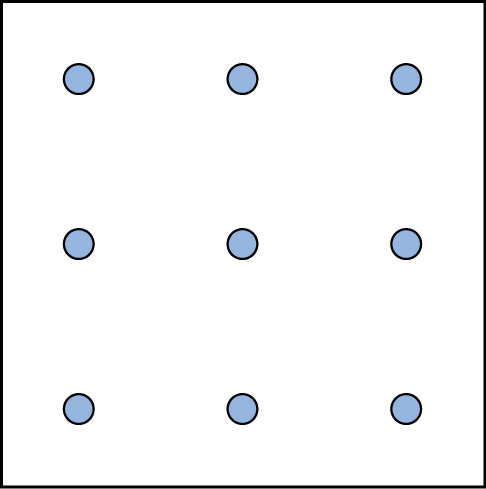
Here is another popular type of puzzle that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
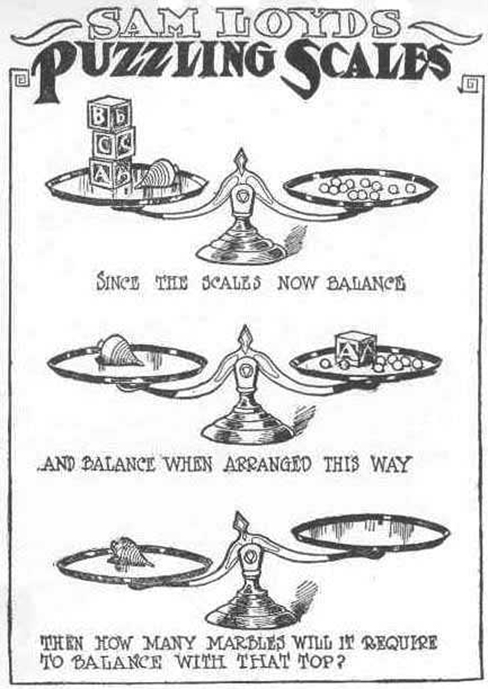
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below. Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Pitfalls to Problem Solving
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of \(\$1,600\). The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for \(\$1,600\) and then shows you a very nice house for \(\$2,000\). Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the \(\$2,000\) home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision. Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in the Table \(\PageIndex{2}\) below.
| Bias | Description |
|---|---|
| Anchoring | Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving |
| Confirmation | Focuses on information that confirms existing beliefs |
| Hindsight | Belief that the event just experienced was predictable |
| Representative | Unintentional stereotyping of someone or something |
| Availability | Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty |
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)? You need nine.
Were you able to solve the problems in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) and Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)? Here are the answers:
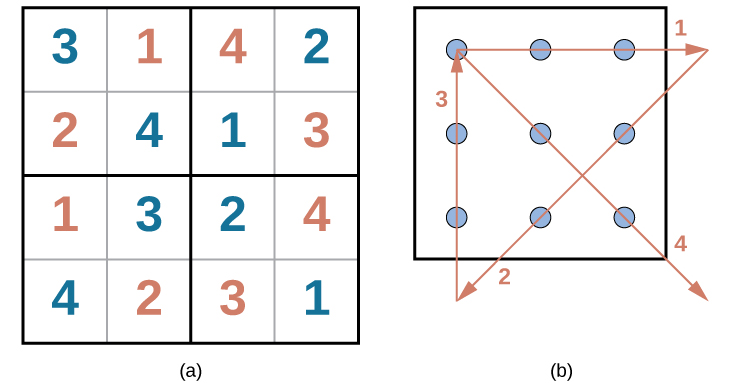
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): Solutions to the puzzles in Everyday Connection
Summary
Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
Glossary
- algorithm
- problem-solving strategy characterized by a specific set of instructions
- anchoring bias
- faulty heuristic in which you fixate on a single aspect of a problem to find a solution
- availability heuristic
- faulty heuristic in which you make a decision based on information readily available to you
- confirmation bias
- faulty heuristic in which you focus on information that confirms your beliefs
- functional fixedness
- inability to see an object as useful for any other use other than the one for which it was intended
- heuristic
- mental shortcut that saves time when solving a problem
- hindsight bias
- belief that the event just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t
- mental set
- continually using an old solution to a problem without results
- problem-solving strategy
- method for solving problems
- representative bias
- faulty heuristic in which you stereotype someone or something without a valid basis for your judgment
- trial and error
- problem-solving strategy in which multiple solutions are attempted until the correct one is found
- working backwards
- heuristic in which you begin to solve a problem by focusing on the end result


