Constantes d'ionisation des acides faibles
- Page ID
- 193999
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
| Constantes d'ionisation des acides faibles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Acide | Formule | K a à 25 °C | Structure de Lewis |
| acétique | CH 3 CO 2 H | 1,8 × 10 −5 |  |
| arsenic | H 3 SO 4 | 5,5 × 10 −3 | 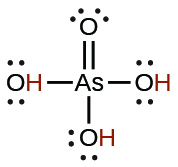 |
 |
1,7 × 10 −7 | ||
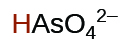 |
5,1 × 10 −12 | ||
| arsénieux | H 3 SO 3 | 5,1 × 10 −10 | 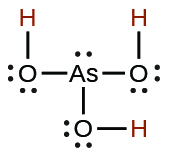 |
| borique | H 3 BOÎTE 3 | 5,4 × 10 −10 | 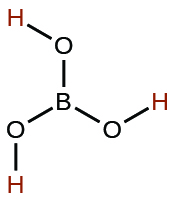 |
| carbonique | H 2 CO 3 | 4,3 × 10 −7 | 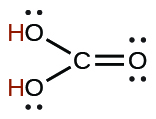 |
 |
4,7 × 10 −11 | ||
| cyanique | HÔ CNO | 2 × 10 −4 | 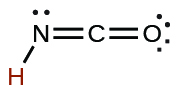 |
| formique | CHO 2 H | 1,8 × 10 −4 |  |
| hydrazoïque | H N 3 | 2,5 × 10 −5 |  |
| cyanhydrique | IL PEUT | 4,9 × 10 −10 | |
| hydrofluorique | H F | 3,5 × 10 −4 | |
| peroxyde d'hydrogène | H 2 OU 2 | 2,4 × 10 −12 | 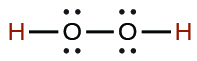 |
| séléniure d'hydrogène | H 2 Sec | 1,29 × 10 −4 | |
| Salut, je vois... | 1 × 10 −12 | ||
| ion sulfate d'hydrogène |  |
1,2 × 10 −2 | 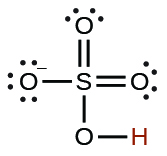 |
| sulfure d'hydrogène | H 2 S | 8,9 × 10 −8 | |
| H S — | 1,0 × 10 −19 | ||
| tellurure d'hydrogène | H 2 Thé | 2,3 × 10 −3 | |
| Salut Te — | 1,6 × 10 −11 | ||
| hypobrome | H BrO | 2,8 × 10 −9 | |
| hypochloreux | H ClO | 2,9 × 10 −8 | |
| nitreux | H N° 2 | 4,6 × 10 −4 | 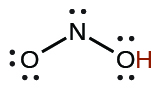 |
| oxalique | H 2 X 2 O 4 | 6,0 × 10 −2 | 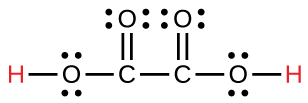 |
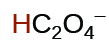 |
6,1 × 10 −5 | ||
| phosphorique | H 3 PO 4 | 7,5 × 10 −3 | 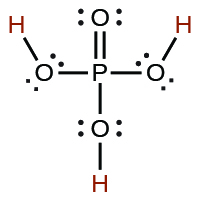 |
 |
6,2 × 10 −8 | ||
 |
4,2 × 10 −13 | ||
| phosphoreux | H 3 OU 3 | 5 × 10 −2 | 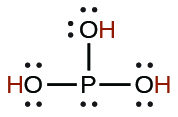 |
 |
2,0 × 10 −7 | ||
| sulfureux | H 2 SO 3 | 1,6 × 10 −2 | 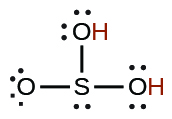 |
 |
6,4 × 10 −8 | ||


